stepper motors
Why stepper motors are used in 3d printers?
One of the main characteristics of stepper motors is that of being able to perform a complete rotation divided into small sections. A complete rotation means a movement of 360° from a starting point on a circumference.
To simplify the concept, let’s imagine that we can turn the shaft of our stepper motor by 1° at a time, to make a complete rotation we will have to “tell” the motor to operate 360 times always in the same direction.
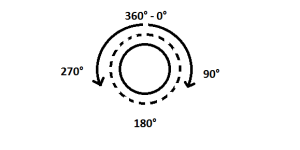
These small movements are the “steps” and we can easily understand that the level of precision that we’re going to get is defintely high. The stepper motors that are used for 3d printers generally have steps of 1.8° which means that to make a complete rotation we will have to operate our motor 200 times (200×1.8° = 360°), therefore we have an excellent level of accuracy.
This precision is used to make really small movements with the moving parts of the 3d printer, this allows a remarkable level of accuracy and detail in our prints.
Continue reading stepper motors →







